How AI Has Transformed BEC (And How You Can Mitigate the Risks)

Author: Matt Findlay, Offensive Services Manager at FRSecure
Large Language Models (LLMs) have been around for quite some time, but the adoption of these tools into everyday business practices has ballooned in recent years.
While these tools can be used quite effectively for things like ideation, outlining, coding, and more, it’s no secret that they come with challenges, concerns, and exploitation.
Probably most notably, Business Email Compromise (BEC), which has already been one of the more successful vectors for cyber attackers, has increased in sophistication and success rate with the help of AI and deepfake technologies.
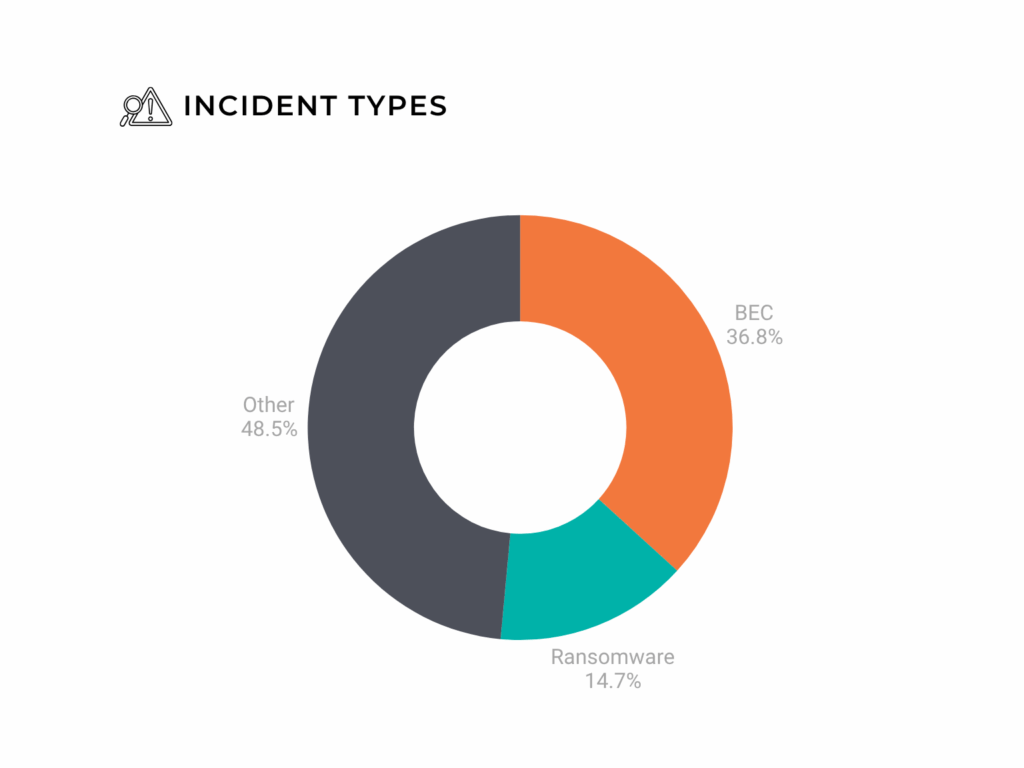 Figure 1: Breakdown of FRSecure’s Recent Incident Response Cases
Figure 1: Breakdown of FRSecure’s Recent Incident Response Cases
Traditionally, BEC involved simple phishing messaging schemes where cybercriminals impersonated coworkers, vendors, and more to manipulate employees into transferring funds or divulging sensitive information.
Now with more tools at their disposal, the threat landscape contains new dimensions to BEC attacks.
Traditionally, an easy way to spot these phishing attempts was through an examination of word choice, tone, spelling, and grammar. But with the onslaught of AI, attackers can now generate highly convincing fake emails, voice recordings, and even video messages. This has made it increasingly difficult for victims to distinguish between legitimate and malicious emails.
The ability of AI to analyze and mimic individual speech patterns, writing styles, and facial expressions has made these attacks more personalized and effective, increasing the likelihood of success.
Perhaps more impactfully, AI-powered tools help automate the creation and distribution of phishing emails, casting a wider net on their targets.
As a result of this unprecedented improvement in attack technique, businesses require more attention to detail and better proactive defense mechanisms.
Understanding the Anatomy of a BEC Attack
Education and awareness are still the best tools we have for identifying and therefore preventing BEC. It is crucial to understand the anatomy of a typical BEC attack, so we know what to be aware of. These attacks generally follow a structured sequence:
- Reconnaissance: Attackers gather information about the target organization, identifying key personnel, their roles, and email addresses. This phase often involves social engineering and data scraping from publicly available sources.
- Initial Compromise: Using techniques such as phishing, malware, or exploiting vulnerabilities, attackers gain access to the email or application accounts of targeted individuals. Managed Service Providers (MSPs) are particularly attractive targets since compromising one MSP can provide access to multiple client networks.
- Email Account Compromise (EAC): Once inside, attackers set up forwarding rules and create fake emails that appear to come from legitimate sources. They monitor email traffic, looking for keywords like “invoice” or “transfer” to identify potential opportunities for fraud.
- Execution: The attackers send fraudulent emails to employees, instructing them to transfer funds, log in to an account, or share sensitive information. These emails often appear urgent or time-sensitive, pressuring the victim to act quickly without verifying the request.
- Monetization: Once the victim complies, the attackers quickly transfer any stolen funds to offshore accounts, making it difficult to trace and recover the money.
The Role of Phishing and Proxy Phishing in BEC
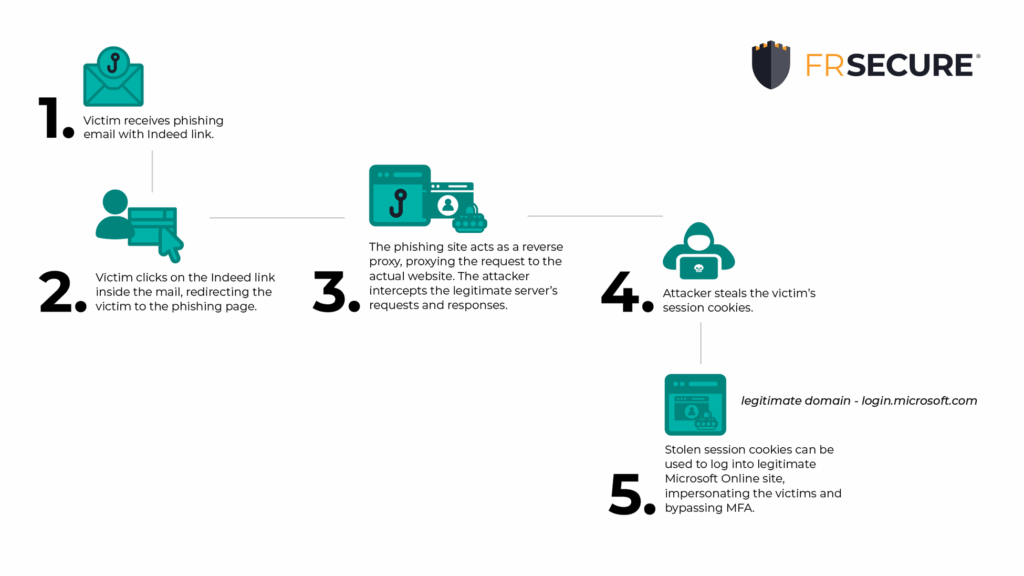
Phishing remains a fundamental component of BEC attacks, serving as the primary method for initial compromise. Now with added AI improvements, attackers craft convincing emails that entice recipients to click on malicious links or download infected attachments, granting the attackers access to their accounts.
Proxy phishing and token theft attacks, particularly through EvilProxy or Phishing-as-a-Service offerings, have further complicated the threat landscape. In proxy phishing, attackers intercept and manipulate legitimate email traffic, redirecting it through their servers to harvest credentials and bypass security measures like multi-factor authentication (MFA). This method allows attackers to maintain a low profile while executing their fraudulent activities.
BEC Prevention Strategies
We touched on the importance of education and awareness in preventing BEC attacks. While this is true, prevention also requires a versatile approach that combines technology and policy enforcement.
Here are some strategies we recommend:
- User Education and Training: Regularly train employees to recognize phishing emails and suspicious activities. Conduct simulated phishing exercises to assess and improve their awareness.
- Conditional Access Policies: Implement conditional access policies that restrict access to sensitive information. Base these restrictions on risk factors like user location, device compliance, and behavior patterns.
- Dual Control for High-Value Transactions: Implement dual authorization for large financial transactions. Require that multiple individuals verify and approve requests before moving forward with payment.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly test an incident response plan to quickly identify, contain, and mitigate the impact of all incidents—including BEC. Utilize templates and guides available from reputable sources, such as the FRSecure IR Plan template and Business Email Compromise Response Playbook.
- Advanced Email Security Solutions: This may sound counterintuitive, but AI does still have positive use cases. Consider advanced email security solutions that leverage AI and machine learning to detect and block phishing attempts, malicious attachments, and abnormal email behaviors.
Trend Predictions and Preparation
As technology continues to evolve, so will the tactics employed by attackers. Businesses must stay ahead of the curve by staying current on trends and preparing for emerging threat advancements. Here are some key areas to watch:
- Increased Use of AI: Expect more sophisticated AI-driven attacks that can adapt and learn from previous attempts. Attackers will only continue to refine and adjust their techniques, making it harder to detect and prevent BEC attacks.
- Deepfake Technology: The use of deepfake audio and video in BEC attacks is expected to rise, creating more convincing impersonations of executives and vendors. Verify the authenticity of communications and teach employees to do the same.
- Monitoring Solutions: While technology is not a silver bullet and must be thoughtfully and thoroughly implemented, tools can help identify and prevent BEC attacks. Consider investing in real-time threat detection and response capabilities.
- Plans, Policies, and Procedures: No one understands your business like you. And while governments and regulatory bodies may introduce new guidelines and requirements for businesses, it remains your responsibility to make risk decisions. Be sure to document, implement, and train on strategies that make sense for your organization.
Information security is a constantly shifting goal post, and organizations must adapt to advancements in attacker techniques and tools. Especially with advancements in LLMs and AI tools, preventing BEC attacks requires thoughtful strategies, tools, and awareness training.
Understand the tools that attackers have at their disposal, recognize the techniques they use to deceive users, and take a proactive approach to avoid or mitigate incidents.
And if you need help with any of that, we’re here for you!